A analysis crew led by Profs. Zhang Zhefeng and Zhang Zhenjun from the Institute of Metallic Analysis of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences has proposed an modern technique to fabricate an anti-fatigue 3D-printed titanium alloy by individually regulating their microstructure and defects, referred to as as net-additive manufacturing preparation (NAMP).
The analysis is revealed within the journal Nature.
Additive manufacturing (AM), often known as three-dimensional (3D) printing, is a disruptive expertise within the manufacturing discipline. Nonetheless, the poor fatigue efficiency of 3D-printed supplies beneath cyclic loading—in contrast with conventional manufacturing—significantly limits the applying of such supplies as structural elements in necessary fields similar to house exploration and aviation.
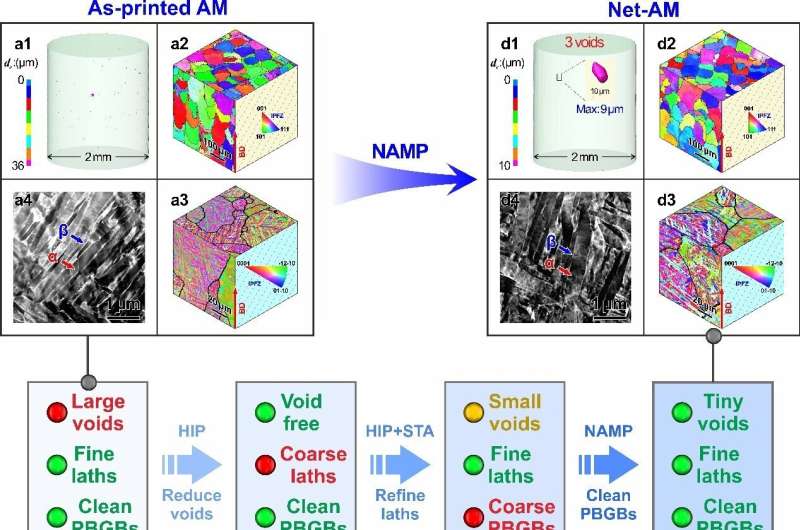
On this research, when it comes to their earlier fatigue prediction theories, the researchers proposed a groundbreaking idea: 3D-printed microstructures (i.e., Internet-AM microstructures) have naturally excessive fatigue resistance. Nonetheless, their low-fatigue efficiency of 3D supplies could also be overshadowed by the destructive results of microvoids induced by the present printing course of.
To confirm this idea, they invented the Internet-Additive Manufacturing Course of (NAMP), together with a hot-isostatic urgent (HIP) to get rid of the microvoids and a subsequent high-temperature-short-time (HTSt) warmth remedy to revive the AM microstructure with superb martensite lath, which may efficiently restore an almost void-free Internet-AM microstructure to the titanium alloy.
Curiously, the Internet-AM microstructure has remarkably excessive fatigue resistance, which exceeds the resistance of all different additively manufactured and even solid titanium alloys. The Internet-AM microstructure additionally reveals the best particular fatigue power (i.e., fatigue power/density) of all reported supplies on this planet.
-
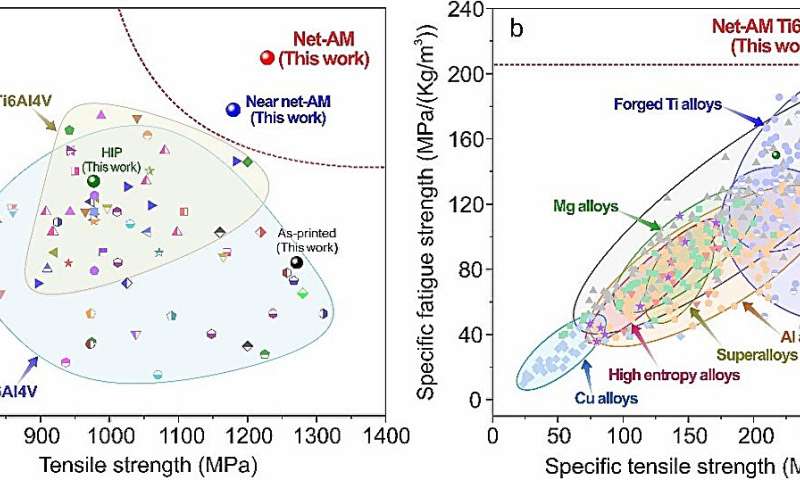
(a) The fatigue power at R = 0.1 vs. tensile power for our work and the Ti-6Al-4V alloys within the literature. (b) Particular power vs. particular fatigue power of our work and different supplies reported within the literature. The present Internet-AM Ti-6Al-4V not solely shows the transcendent fatigue power over each the AMed and solid Ti-6Al-4V alloys but in addition shows the best particular fatigue power amongst all supplies. Credit score: IMR
-
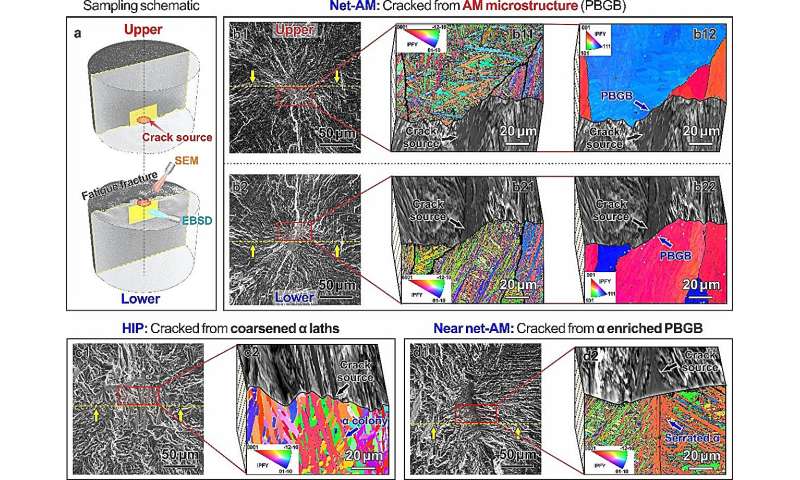
(a) Schematic illustration for our exact sectioning approach on the placement of fatigue crack initiation; most stress and cycles to failure for (b) NAMP state; (c) HIP state; (d) HIP+STA state. The fatigue cracks of the NAMP state provoke from the clear PBGBs, which is a standard attribute within the AM microstructure, indicating that we now have detected the fatigue resistance of the Internet-AM microstructure. Credit score: IMR
The fatigue cracks of the microstructures ready utilizing the NAMP course of usually nucleated at clear main β grain boundaries and superb martensite lath, efficiently avoiding many conventional fatigue weaknesses and stopping localized injury accumulation, thus exhibiting extraordinarily excessive fatigue resistance.
This research reveals the naturally excessive fatigue resistance of the 3D-printed microstructure and the potential benefits of 3D printing expertise within the manufacturing of structural elements, and likewise factors out clear instructions for 3D printing anti-fatigue manufacturing.
Extra info:
Robert Ritchie, Excessive fatigue resistance in a titanium alloy through near-void-free 3D printing, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07048-1. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07048-1
Chinese language Academy of Sciences
Quotation:
Scientists suggest anti-fatigue preparation for 3D-printed titanium alloy (2024, February 28)
retrieved 28 February 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-02-scientists-anti-fatigue-3d-titanium.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.