Within the quickly evolving world of 3D printing, the pursuit of quicker, extra environment friendly and versatile manufacturing strategies is unending. Conventional 3D printing strategies, whereas groundbreaking, are sometimes time-consuming and restricted within the sorts of supplies they will use as feedstock.
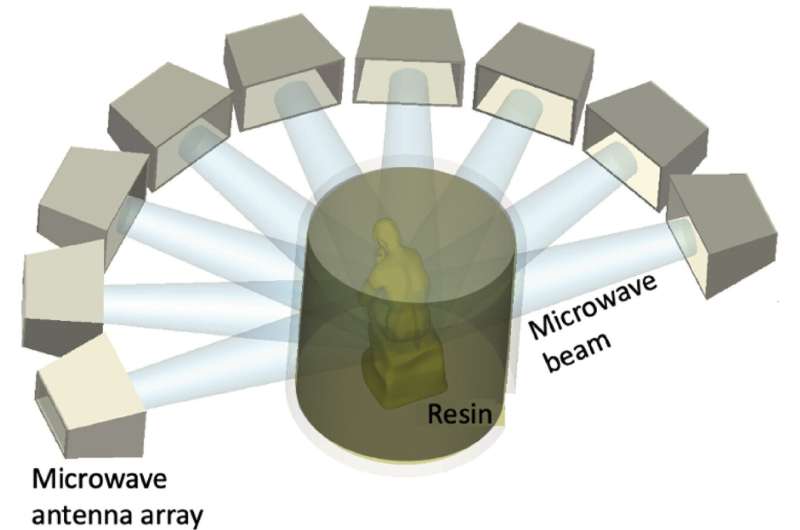
However, by means of a brand new course of a Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory (LLNL) staff is looking Microwave Volumetric Additive Manufacturing (MVAM), researchers have launched an revolutionary new method to 3D printing utilizing microwave vitality to remedy supplies, opening the door to a broader vary of supplies than ever earlier than.
In a current paper revealed in Additive Manufacturing Letters, LLNL researchers describe the potential of microwave vitality to penetrate a wider vary of supplies in comparison with light-based volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM).
Whereas VAM strategies like Computed Axial Lithography permit for fast printing of complicated 3D shapes in a single operation and eradicate the necessity for assist constructions, VAM depends on particular supplies, primarily clear and low-absorbing resins, which restricts using opaque or composite supplies.
In comparison with projected gentle, microwaves can attain deeper into supplies, making them a super candidate for curing quite a lot of resins, together with resins which might be opaque or loaded with components, researchers mentioned. This functionality may considerably improve the flexibility of 3D printing, permitting for the creation of extra complicated, practical and bigger elements, based on LLNL analysis scientist Saptarshi Mukherjee, who co-led the paper with Lab supplies chemist Johanna Schwartz.
“I feel that is going to revolutionize the best way folks have a look at additive manufacturing,” mentioned Mukherjee, who focuses on utilized electromagnetics. “If we take into consideration plenty of functions—aerospace, automotive, nuclear business—their geometries are easy, however they’re massive and so they want fast prototyping.
“One main influence [of MVAM] is that if we are able to preserve a feedstock of supplies surrounded with a microwave antenna array, we are able to now take into consideration creating easy massive geometries, in addition to difficult massive geometries, at scale utilizing microwaves.”
Co-author Maxim Shusteff, co-inventor of the unique seen light-based CAL method, mentioned the power to rapidly produce elements with massive geometries may very well be a recreation changer for additive manufacturing.
“Microwave volumetric AM opens up a brand new frontier in 3D printing by enabling using opaque and stuffed supplies, which have been beforehand difficult to work with,” Shusteff mentioned, “This is usually a path towards large-format elements with enhanced materials properties.”
A breakthrough in curing know-how
To discover the potential of microwave VAM, the analysis staff at LLNL developed a multi-physics computational mannequin of the microwave beams, designed to optimize energy supply and curing time and guarantee higher thermal management throughout the printing course of. By simulating how microwaves work together with totally different supplies, the staff can predict how successfully they will remedy numerous resins.
The researchers validated their mannequin utilizing a proof-of-concept experimental system and demonstrated the power to remedy all kinds of supplies, together with each optically translucent and opaque epoxy resins.
The outcomes have been spectacular: whereas present microwave {hardware} working at 40 watts may remedy resins in about 2.5 minutes, the mannequin advised that curing occasions may very well be diminished to as little as six seconds at one-kilowatt energy ranges—about the identical quantity of vitality as a typical microwave oven.
This functionality may probably velocity up the manufacturing course of and permit for the creation of bigger elements, researchers mentioned. The staff discovered that their method can print options starting from a couple of millimeters to twenty millimeters, with the potential to scale as much as meter-sized constructions sooner or later.
The multi-physics mannequin permits researchers to visualise how microwave vitality propagates by means of supplies and the way it impacts the curing course of. By understanding properties of various supplies, the staff was capable of fine-tune the microwave vitality to realize optimum outcomes, researchers reported.
Co-principal investigator Schwartz, the staff’s chemistry lead, mentioned that whereas conventional (optical) VAM is proscribed by the necessity for clear, low-absorbing photoresins, with microwave VAM, “an entire new world of printing supplies turns into potential.”
“With have a singular alternative to increase the definition of what’s ‘printable,’ accessing chemistries beforehand not potential in light-based techniques,” Schwartz mentioned. “It is a entire new printing area, and so our ongoing progress is simply extraordinarily thrilling.”
Mukherjee added that researchers may apply the identical ideas utilized in optical VAM, however accomplish that with “an array of antennas and beamforming algorithms” as an alternative of a typical gentle projector.
“We’re creating the total antenna array system with beamforming algorithms and we’re particularly taking a look at ceramic supplies due to their inaccessibility by standard VAM and in addition due to their promise in numerous high-temperature, high-pressure sorts of environments,” Mukherjee mentioned.
Researchers mentioned the implications of the work may prolong far past the Laboratory. The flexibility to remedy a wider vary of supplies rapidly and effectively may very well be transformative in industries akin to aerospace, automotive and well being care. For example, producers may create complicated parts with built-in functionalities, akin to sensors or conductive pathways, all in a single printing course of.
As well as, the potential for utilizing opaque and composite supplies implies that merchandise could be designed with enhanced properties, akin to improved energy, thermal resistance or electrical conductivity. This versatility may result in the event of fully new merchandise and functions that have been beforehand unimaginable, based on the researchers.
Because the staff continues to refine their MVAM system, they envision a future the place multi-antenna arrays can be utilized to additional improve the curing course of and make manufacturing extra environment friendly and able to producing a wider array of supplies at unprecedented speeds, pushing the boundaries of what is potential in AM.
However first, researchers might want to work out how you can make the method cheaper, and probably spin the know-how out to business. Future work additionally goals to include particle-scale results into the mannequin, additional enhancing its predictive capabilities.
“Excessive-power microwave units are extraordinarily costly—a one-kilowatt pulsed microwave amplifier system may value between $50,000 and $100,000,” Mukherjee mentioned.
“We’re taking a look at how we are able to customized design or customized construct a few of these circuits or {hardware} by ourselves in order that we are able to scale back plenty of value and present that the general idea works earlier than large initiatives or outdoors exterior sponsors are prepared to take a position on this know-how.”
Extra info:
Saptarshi Mukherjee et al, In the direction of microwave volumetric additive manufacturing: Technology of a computational multi-physics mannequin for localized curing, Additive Manufacturing Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.addlet.2024.100209
Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory
Quotation:
Revolutionizing 3D printing by means of microwave know-how (2024, September 4)
retrieved 4 September 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-09-revolutionizing-3d-microwave-technology.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

